1.3 KiB
1.3 KiB
Overview
This document will provide some insight into the known_gaps table, their use cases, and implementation. Please refer to the following PR and the following epic to grasp their inception.
Use Cases
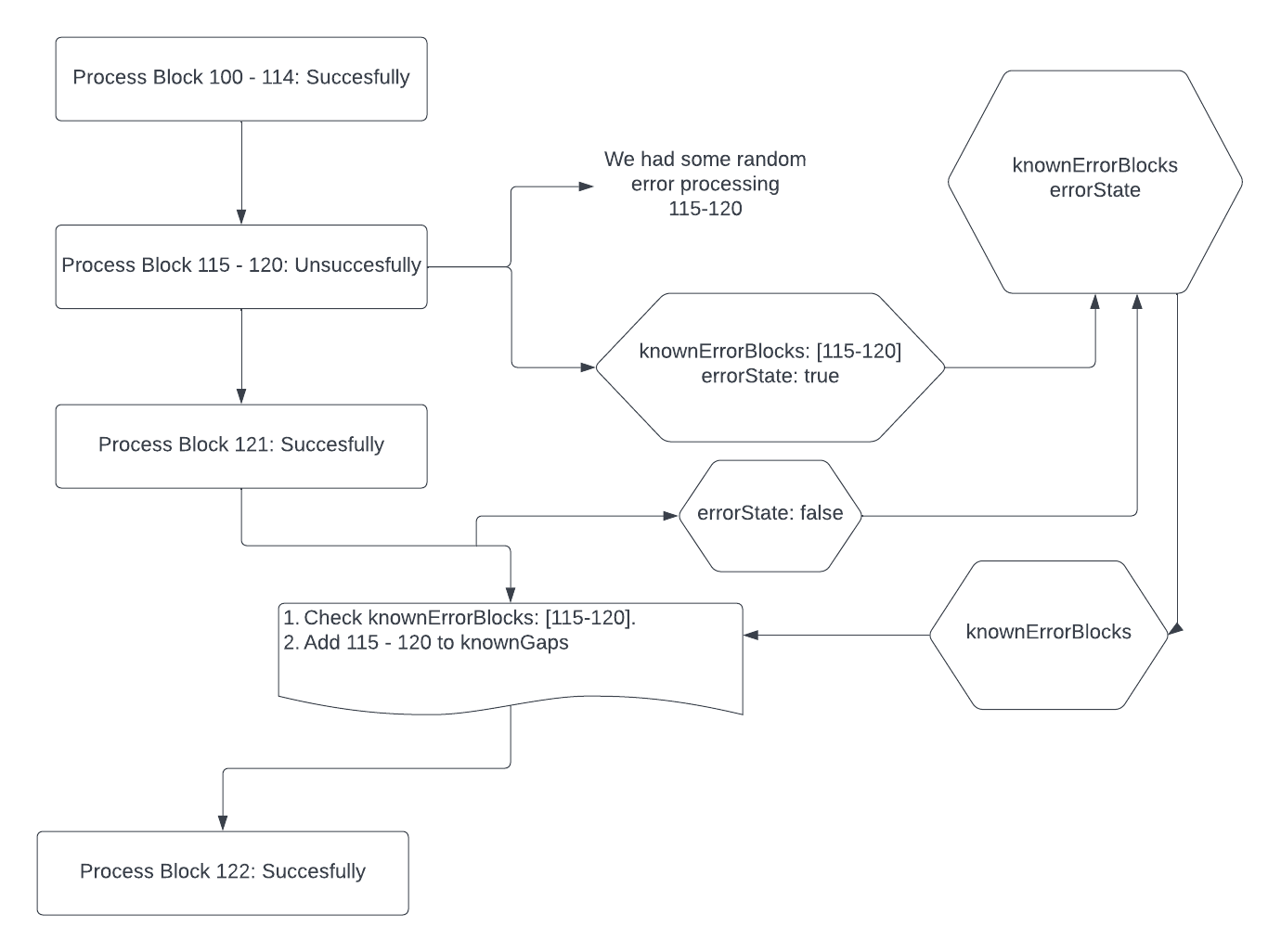
The known gaps table is updated when the following events occur:
- At start up we check the latest block from the
eth.headers_cidtable. We compare the first block that we are processing with the latest block from the DB. If they are not one unit of expectedDifference away from each other, add the gap between the two blocks. - If there is any error in processing a block (db connection, deadlock, etc), add that block to the knownErrorBlocks slice, when the next block is successfully written, write this slice into the DB.
Glossary
expectedDifference (number)- This number indicates what the difference between two blocks should be. If we are capturing all events on a geth node then this number would be1. But once we scale nodes, theexpectedDifferencemight be2or greater.processingKey (number)- This number can be used to keep track of different geth nodes and their specificexpectedDifference.